How to Prevent and Treat Mpox

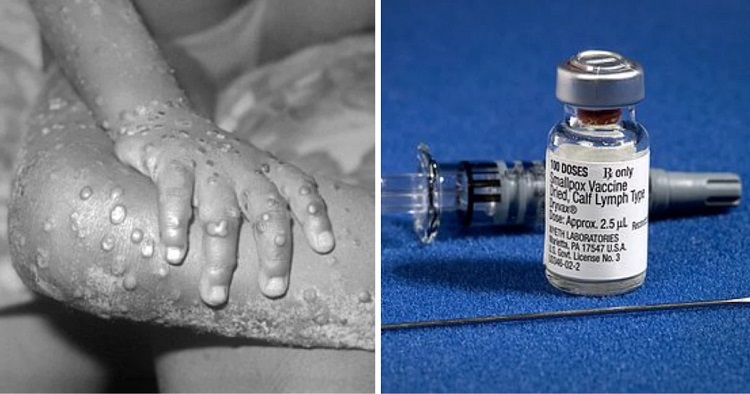
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is a rare viral disease caused by the mpox virus. Although it was initially found in Central and West Africa, the disease has spread to other parts of the world, due to factors like international travel and close contact with infected individuals. With the outbreak of mpox in 2022, it's more important than ever to understand how to prevent and treat this illness. Let’s learn about the most effective ways to prevent and treat mpox.
What Is Mpox?
Mpox is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. It is caused by the mpox virus, which typically affects rodents and non-human primates. The disease is similar to smallpox but usually less severe.
Mpox is characterized by a fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes, with symptoms lasting 2 to 4 weeks. The disease can be severe, leading to complications such as severe scarring, blindness, and even death in rare cases.
How Does Mpox Spread?
Mpox spreads through close contact with an infected person or animal. It can also spread through handling materials like bedding or clothing contaminated with the virus. The virus can be transmitted from person to person through:
- Direct contact with an infected person's rash, scabs, or body fluids.
- Extended close contact with respiratory droplets, including sexual contact.
- Contact with contaminated objects, such as clothes or blankets.
How to Prevent Mpox
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of mpox. By taking the following steps, you can reduce your risk of infection:
Avoid Close Contact with Infected Individuals
If you know someone who has been diagnosed with mpox, avoid close physical contact with them until they have fully recovered. Mpox is most contagious when the infected person shows symptoms, particularly when they have a rash.
Use Protective Measures
If you must be in contact with someone who has mpox, wear personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and gowns. This is especially important for healthcare workers and those caring for infected individuals at home.
Practice Good Hygiene
Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coming into contact with an infected person or animal. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
Avoid Contact with Potentially Infected Animals
Mpox can also spread from animals to humans. Avoid contact with animals that may carry the virus, such as rodents or non-human primates. Do not handle or consume wild game that may be infected, and avoid contact with animal products, such as furs, that could be contaminated.
Disinfect Contaminated Items
If you have been in contact with an infected person or animal, disinfect any objects or surfaces that may have been contaminated. Use a bleach solution or other disinfectant to clean clothing, bedding, and other items.
Get Vaccinated
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent mpox. The smallpox vaccines, such as ACAM2000 and Jynneos, have been shown to protect against mpox because of the close relationship between the smallpox and mpox viruses.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends vaccination for those who have been exposed to pox or are at high risk of exposure.
Isolate Infected Individuals
If someone in your household has mpox, isolate them in a separate room to prevent the virus from spreading to others. Ensure they use separate bathroom facilities if possible, and do not share personal items like towels or bedding.
Practice Safe Sex
Since mpox can spread through sexual contact, it's important to practice safe sex, especially if you or your partner have been exposed to the virus. Use condoms and dental dams to reduce the risk of transmission.
How to Treat Mpox
While there is no specific cure for mpox, the disease is usually self-limiting, meaning it resolves on its own with proper care. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
Symptom Management
The primary goal of treatment is to manage the symptoms of mpox. This includes:
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce fever and alleviate pain.
Skin Care: The mpox rash can be itchy and uncomfortable. Taking oatmeal baths can help soothe the skin and reduce itching. Applying topical treatments recommended by a healthcare provider can also help.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids is essential to prevent dehydration, especially if you have a fever. Staying hydrated also helps keep your skin healthy as it heals from the rash.
Isolation and Rest
If you have mpox, it's crucial to isolate yourself from others to prevent spreading the virus. Stay home, rest, and avoid contact with other people and pets until all lesions have healed. Cover any open sores with bandages or gauze to prevent the spread of the virus.
Antiviral Medications
In severe cases, or for individuals with weakened immune systems, healthcare providers may prescribe antiviral medications like tecovirimat (TPOXX) or cidofovir. These medications are approved for treating smallpox and may be effective against mpox, but more research is needed to confirm their efficacy.
Preventing Secondary Infections
Mpox can lead to secondary bacterial infections, especially if the skin is broken due to scratching. If a secondary infection develops, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to prevent further complications.
Monitoring and Support
If you have been diagnosed with mpox, your healthcare provider will monitor your condition and provide support as needed. This may include regular check-ins to ensure your symptoms are improving and to address any complications that may arise.
Immune Globulin Therapy
For individuals who are unlikely to respond to the vaccine or antiviral treatments, healthcare providers may consider using vaccinia immune globulin (VIG), which contains antibodies from people who have received the smallpox vaccine. This therapy can help boost the immune system's response to the virus.
Conclusion
Mpox is a serious disease that requires careful attention to prevention and treatment. By understanding how the virus spreads and taking steps to protect yourself and others, you can reduce the risk of infection.
If you do contract mpox, focusing on symptom management and isolation can help you recover safely. Stay informed, practice good hygiene, and consult your healthcare provider if you suspect you have been exposed to or infected with mpox.
